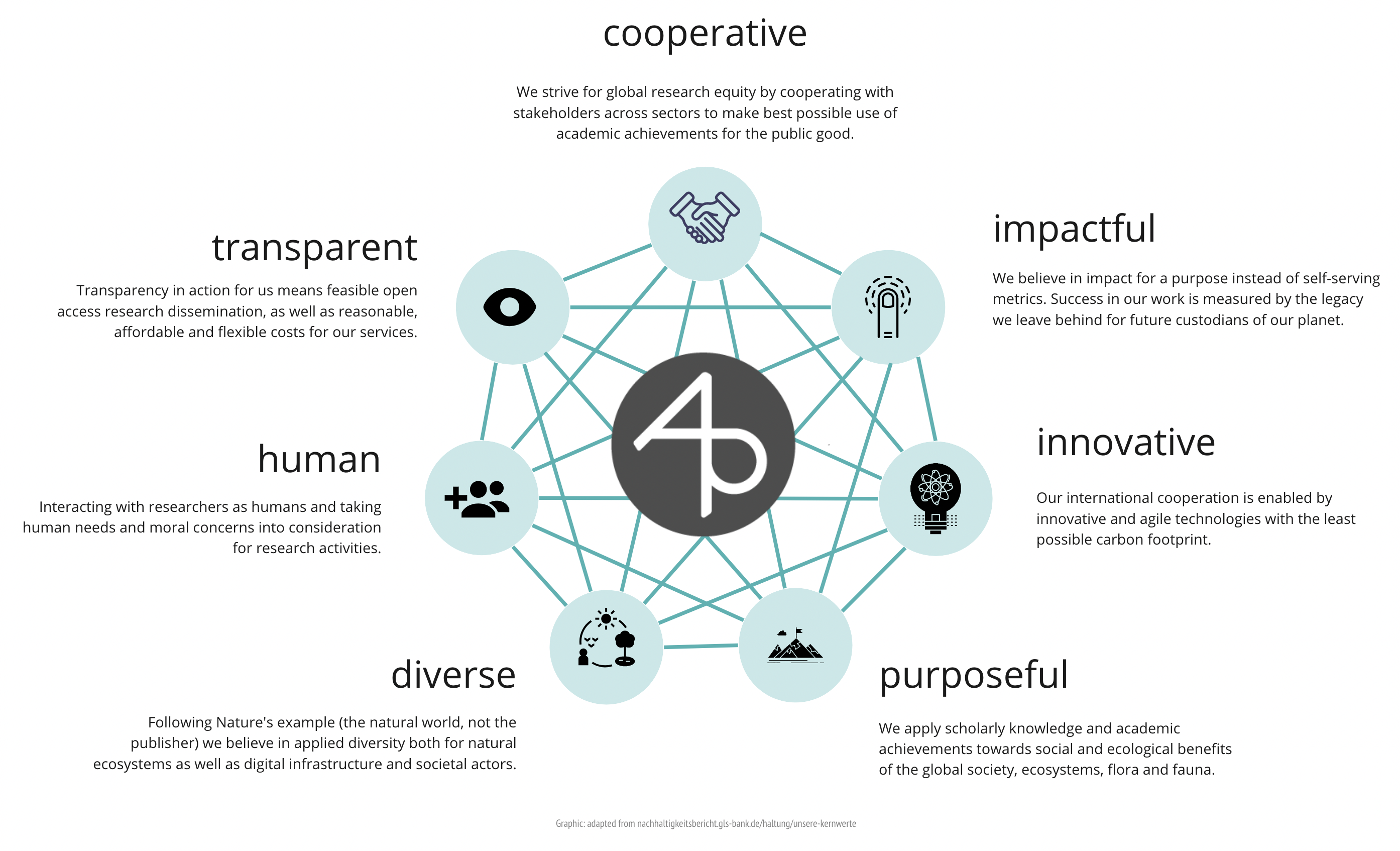
At Access 2 Perspectives, we are committed to human rights, equity, and ecological sustainability.
The foundations of our work as scholars, entrepreneurs, and researchers are based on respect for the diversity of life and nature and concern for the peaceful coexistence of all cultures, based on individual freedom and responsibility.
Our actions are intended to preserve the natural foundations of life for present and future generations and to promote their further protection and restoration. We understand ecology holistically in the sense of a unity of nature and the development of civilization, the goal of which is to protect and preserve life.
We collaborate and cooperate with people and organizations who pursue ecological, social, or cultural goals and want to creatively help positively influence our societies and ecosystems. Together with them, we develop new forms of research and innovation engagements that are determined by solidarity and responsibility for our environment on this planet.
We live and act by our moral standards as is reflected in the projects we engage in, the partnerships we build and maintain as well as the tools we use.
Below are a few examples:
Human Rights

Universal Declaration of Human Rights
Article 27
1. Everyone has the right freely to participate in the cultural life of the community, to enjoy the arts and to share in scientific advancement and its benefits.
2. Everyone has the right to the protection of the moral and material interests resulting from any scientific, literary or artistic production of which he is the author.

UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples
Article 31
1. Indigenous peoples have the right to maintain, control, protect and develop their cultural heritage, traditional knowledge and traditional cultural expressions, as well as the manifestations of their sciences, technologies and cultures, including human and genetic resources, seeds, medicines, knowledge of the properties of fauna and flora, oral traditions, literatures, designs, sports and traditional games and visual and performing arts. They also have the right to maintain, control, protect and develop their intellectual property over such cultural heritage, traditional knowledge, and traditional- al cultural expressions.
2. In conjunction with indigenous peoples, States shall take effective measures to recognize and protect the exercise of these rights.
Fostering Open Research and Publishing Practices
Our recommendations and training programs are aligned with the UNESCO Open Science Recommendation and adhere to Open Science facilitating scholarly principles, standards, and best practices.
Animal Welfare

“Animal welfare is a complex and multi-faceted subject with scientific, ethical, economic, cultural, social, religious and political dimensions. […]”
It is attracting growing interest from civil society and is one of the priorities of the OIE. The OIE, at the request of its Member Countries, is the international organisation responsible for setting standards on this topic.
The OIE Global Animal Welfare Strategy was developed from lessons learned from actions taken at national and regional level and aims to be a source of ongoing guidance for the OIE’s activities in this area. Adopted in 2017 by all Member Countries, it was developed with the objective of achieving: “A world where the welfare of animals is respected, promoted and advanced, in ways that complement the pursuit of animal health, human well-being, socio-economic development and environmental sustainability”.
The strategy focuses on the development of international standards on animal welfare, in consultation with Member Countries and key international stakeholders, developing the capacity of Veterinary Services, improving communication with governments and raising awareness around the issue, and, finally, supporting Member Countries in the implementation of these standards.
Read more at oie.int/en/what-we-do/animal-health-and-welfare/animal-welfare/
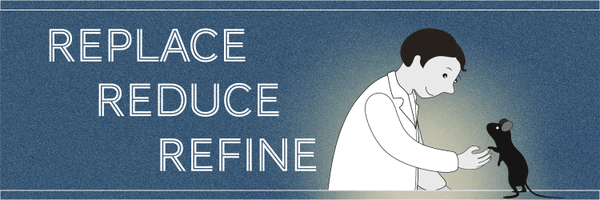
The BfR performs the role of the “German Centre for the Protection of Laboratory Animals (Bf3R)” and coordinates all associated activities nationwide with the goal of:
- Reducing animal experiments to the necessary minimum
- Providing the best possible protection for laboratory animals.
Furthermore, national and international research activities and a scientific dialogue shall be encouraged by the work of the Centre.
Mission and goals of the German Centre for the Protection of Laboratory Animals (Bf3R)
- Intensifying research on alternative methods
- Advice to authorities and research institutions
- International harmonisation of alternative methods
- Research funding of alternative methods
- Provision of information to the public and experts
The activities of the German Centre for the Protection of Laboratory Animals are part of the Animal Welfare Initiative of the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (BMEL) entitled “Minding animals – new ways to improve animal welfare”.
Read more at bfr.bund.de/en/german_centre_for_the_protection_of_laboratory_animals.html
Our Digital Infrastructure
We have deployed this website and database on 100% green energy because sustainability matters—online and offline. Thanks to our partner WindCloud, our carbon footprint is actually negative!
All files, including sensitive GDPR-protected data, are stored in their data centre in Northern Germany, powered entirely by wind energy. Even better: the excess heat from the data centre is used to grow algae for food supplements, turning energy use into a sustainable by-product.
Learn more about green/eco-friendly hosting at en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Green_hosting.
GDPR compliance
To ensure data security and privacy, all our operations strive to align with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to the best of our capacity and knowledge. Read more about GDPR compliance at gdpr.eu.
Balancing between ethical concerns and functionality
With the digital tools and services accessible online, we look at ethical standards, data security and privacy levels, environmental impact, and reliability differences.
Please e-mail us in case of any questions and if you have recommendations.